Setting up Pyspark in Jupyter through Homebrew on Mac M1
This is more of a “write it down in case I forget it” kind of post. When I switched to Mac I had to figure out how to install things with Homebrew, and doing that somehow involved more random things I had to tinker with just to get stuff working. Anyway, I wanted to set up Pyspark on my Mac with an M1 processor. And because it seemed rather complicated when I was doing it, I had to write it all down so that I wouldn’t forget. Looking back, the steps aren’t actually that complicated :__).
Install Homebrew
If you don’t already have Homebrew installed in your Mac, install it through this command:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
If that doesn’t work, I recommend checking the homebrew website to get the correct up-to-date command to install Homebrew.
Install Java and set JAVA_HOME
Java is required for Pyspark to run. Some articles would tell you to install openjdk@8 (version 8 JDK version), but that wouldn’t work on M1’s processor architecture. So instead, install version 11:
brew install openjdk@11
Then take note where your java is installed:
which java
This should point you to a path in brew, something like this:
/opt/homebrew/opt/openjdk@11/bin/java
Copy this path and set your JAVA_HOME environment variable accordingly in your ~/.zshrc file:
export JAVA_HOME="/opt/homebrew/opt/openjdk@11/"
Important: Note that the bin/java part has been removed from the path.
Then execute your ~/.zshrc file to make the environment variable available in your terminal sessions:
source ~/.zshrc
Install python
If you don’t already have Python installed in your system, you can install the latest version with Homebrew:
brew install python
If you are using pyenv, no need to install python through homebrew, as this might cause a conflict with the python version that you want to use. Instead, you would want to just spin up a local pyenv version in your current directory, like this (for example, installing version 3.10.10 on your local directory):
pyenv local 3.10.10
Install apache-spark
Now that you have Java and Python installed, you can now install Pyspark:
brew install apache-spark
When this installation finishes, check the installation output text. You should be able to find the path where pyspark was installed in brew. Something like this:
/opt/homebrew/Cellar/apache-spark/3.3.2
Take note of this path then set your SPARK_HOME accordingly in your ~/.zshrc file:
export SPARK_HOME="/opt/homebrew/Cellar/apache-spark/3.3.2/libexec"
Important: Note the added “libexec” at the end of the path. This is apparently needed on Mac installations.
Then execute your ~/.zshrc file to make the environment variable available in your terminal sessions:
source ~/.zshrc
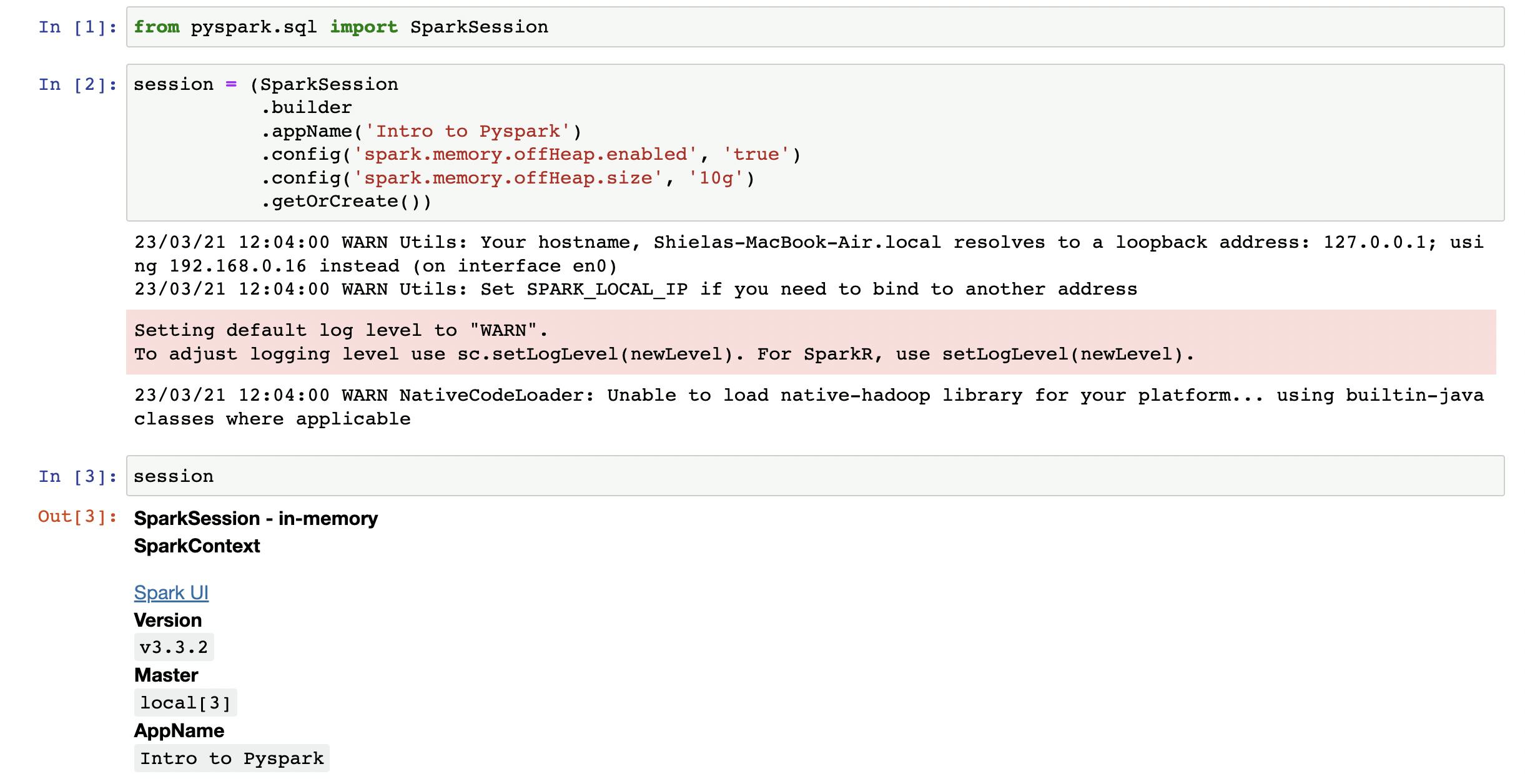
You can verify the pyspark installation by typing pyspark on your terminal, which will start a new Pyspark session:
(venv) shiela@Macbook spark-project % pyspark
Python 3.10.10 (main, Mar 2 2023, 22:59:21) [Clang 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/__ / .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 3.3.2
/_/
Using Python version 3.10.10 (main, Mar 2 2023 22:59:21)
Spark context Web UI available at http://192.168.0.16:4040
Spark context available as 'sc' (master = local[*], app id = local-1679398716738).
SparkSession available as 'spark'.
There may be a few WARNING messages, but you can ignore those for now.
To exit the Pyspark session, just type exit(), and you will be taken back to your terminal.
Install jupyter
Ok, we’re almost done! We now only have to install and jupyter notebook. You can install jupyter either through Homebrew:
brew install jupyter
or by using pip:
pip install jupyter
If you’re using pyenv and working inside a virtual environment, better to install through pip as this will install jupyter within your pyenv environment instead of globally throughout your system.
After installation, you can now run jupyter:
jupyter notebook
This will open a new jupyter notebook session in your browser. You can then run a pyspark session by instatiating the SparkSession object: